
ALLOCATING MORE MEMORY INTO CLC GENOMICS WORKBENCH SKIN
In support of recirculation, CD4 + T cells expressing intermediate levels of CCR7 and CD62L have been shown to egress from the skin of specific pathogen–free (SPF) mice ( Bromley et al., 2013). Similarly, after Candida albicans infection, mouse skin was shown to harbor both resident and migratory CD4 memory T cells ( Park et al., 2018). Follow-up studies indicated that memory CD4 + T cells in resting mouse skin equilibrated with circulation, although there was a biased retention of perifollicular CD4 + T cells after herpes simplex virus infection, and inflammation altered the equilibration set-point ( Collins et al., 2016). However, firm evidence for CD4 + T RM in the reproductive mucosa has been reported ( Iijima and Iwasaki, 2014 Stary et al., 2015). Moreover, early reports documenting CD8 + T RM in skin highlighted that CD4 + memory T cells were almost entirely comprised of a recirculating population in the skin and reproductive mucosa ( Gebhardt et al., 2011), establishing a precedent that CD8 + and CD4 + T cells may obey fundamentally different rules of NLT immunosurveillance. Moreover, the proportion of blood-borne memory CD4 + T cells that express an effector memory phenotype is often higher than observed for CD8 + T cells, which may be consistent with nonlymphoid recirculation strategies ( Nascimbeni et al., 2004). First, antiviral antigen-specific memory CD4 + T cells are typically much less abundant than their CD8 + T cell counterparts ( Seder and Ahmed, 2003 Surh and Sprent, 2008 Taylor and Jenkins, 2011), and thus may require different strategies for patrolling the organism for evidence of reinfection.

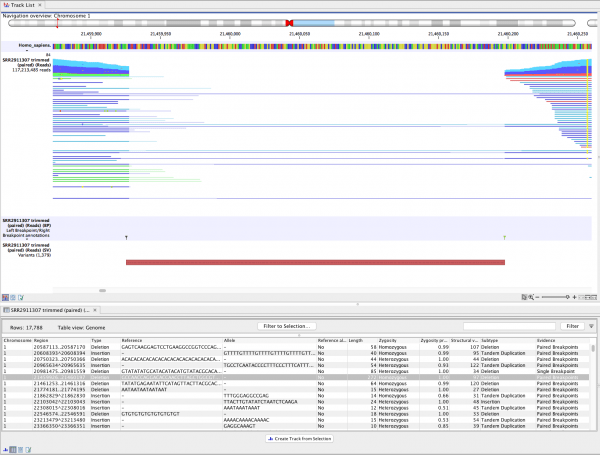
The extent to which residence contributes to global memory CD4 + T cell surveillance is less clear. Thus, residence provides a dominant mechanism for regionalizing CD4 + T cell immunity, and location enforces shared transcriptional, phenotypic, and functional properties with CD8 + T cells. Functionally, mucosal CD4 + T RM reactivation locally triggered both chemokine expression and broad immune cell activation. CD4 + and CD8 + T RM shared overlapping transcriptional signatures and location-specific features, such as granzyme B expression in the small intestine, revealing tissue-specific and migration property–specific, in addition to lineage-specific, differentiation programs. Migration properties of memory-phenotype CD4 + T cells in non-SPF parabionts were similar, generalizing these results to diverse infections and conditions. In contrast, memory CD4 + T cells were more likely to be resident within lymphoid organs than CD8 + T cells. After acute viral infection, memory CD4 + T cells predominantly used residence to survey nonlymphoid tissues, albeit not as stringently as observed for CD8 + T cells. Plugins and modules add a layer of specialized tools and workflows to CLC Genomics Workbench, creating a comprehensive solution for microbial genomics and metagenomics data analysis.This study examines the extent to which memory CD4 + T cells share immunosurveillance strategies with CD8 + resident memory T cells (T RM). QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench Premium expands upon CLC Genomics Workbench, the industry-standard platform for bioinformatics computing. Due to preconfigured workflows that streamline processing of raw NGS data, researchers can focus on the interpretation of results, for example in the context of other samples or metadata. Data and sample-metadata management is included. All analytics for microbial genomics and metagenomics come fully integrated into one scalable and enterprise-ready solution. QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench Premium provides integrated analytics that deliver research continuity. Yet a lack of well integrated analytics for microbial genomics leaves researchers and organisations with the burden of integrating and maintaining all the required bioinformatics, statistics and visualisation tools required to power their research. From data to discovery with QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench PremiumĮver-growing sample volumes demand efficient bioinformatics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
